Panic attack vs anxiety attack: A comprehensive guide to understanding the symptoms, triggers, duration, management techniques, treatment options, and key differences between these two common mental health conditions. Explore the complexities of panic and anxiety with liputan6 author style.
Delve into the intricacies of panic attacks and anxiety attacks, uncovering their distinct characteristics and the nuances that set them apart. Gain insights into their triggers, durations, and intensities, empowering you with knowledge to effectively manage these conditions and improve your mental well-being.
Panic Attacks vs Anxiety Attacks
Panic attacks and anxiety attacks are two distinct conditions that can cause significant distress and disruption to daily life. While they share some similarities, there are also key differences between the two. Understanding these differences can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and manage their symptoms effectively.
Symptoms
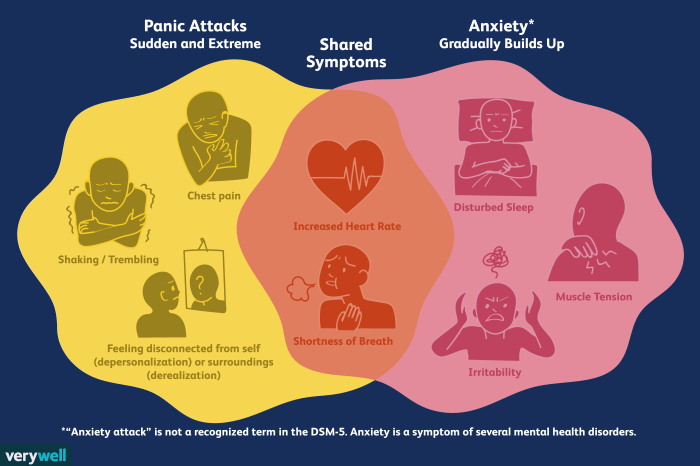
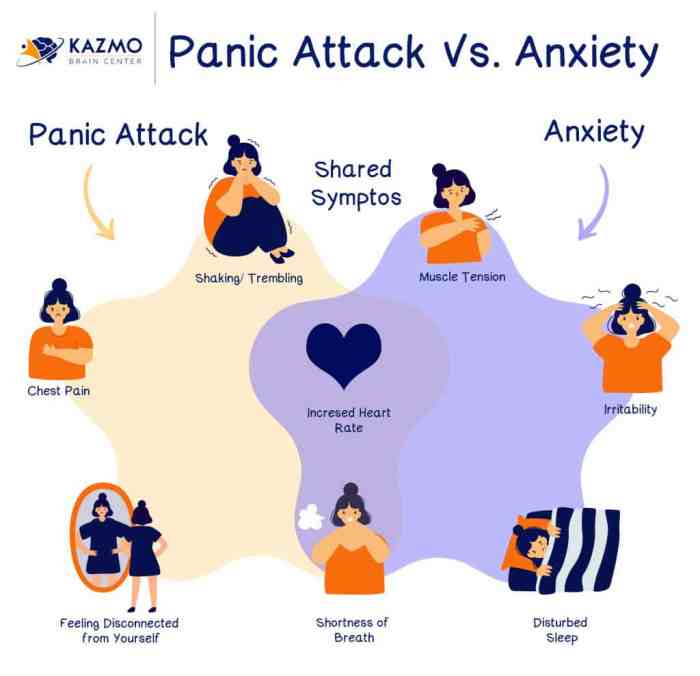
Panic attacks are characterized by a sudden onset of intense fear or discomfort that peaks within minutes. They are often accompanied by physical symptoms such as:
- Rapid heart rate
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath or hyperventilation
- Sweating
- Nausea or vomiting
- Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
Anxiety attacks, on the other hand, are characterized by more persistent and generalized feelings of worry, nervousness, or fear. Physical symptoms may also be present, but they are typically less severe than those experienced during panic attacks.
- Muscle tension
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Sleep disturbances
Triggers
Panic attacks can be triggered by a variety of factors, including:
- Stress
- Fear
- Certain situations or objects (e.g., heights, enclosed spaces)
- Physical illness or substance abuse
Anxiety attacks can also be triggered by stress, but they are more likely to occur in response to everyday events or situations that cause worry or anxiety.
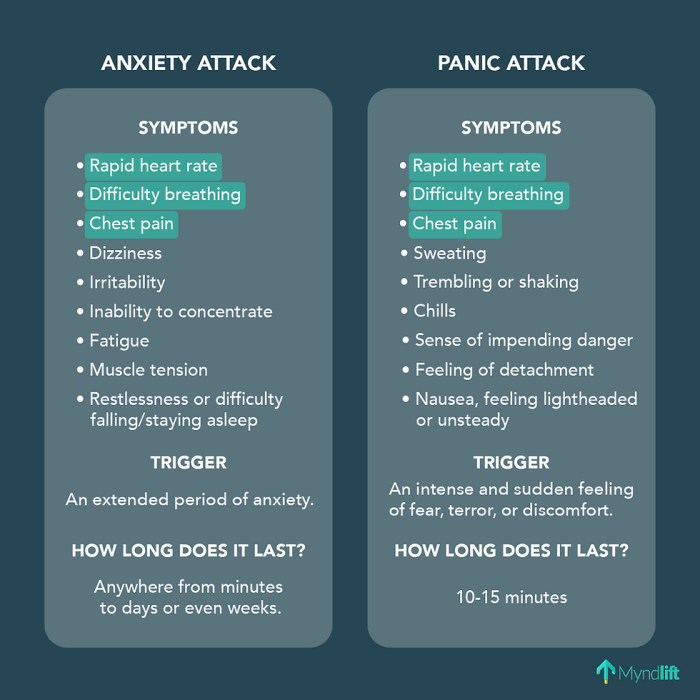
Duration and Severity
Panic attacks typically last for a few minutes to an hour. Anxiety attacks can last for longer periods of time, ranging from hours to days.
The severity of symptoms can vary between individuals. Some people may experience mild panic attacks or anxiety attacks, while others may experience severe attacks that significantly interfere with their daily lives.
Management Techniques, Panic attack vs anxiety attack
There are several effective coping mechanisms for managing panic attacks:
- Deep breathing exercises
- Relaxation techniques (e.g., yoga, meditation)
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Exposure therapy
- Medication (e.g., antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications)
For anxiety attacks, similar coping mechanisms can be helpful:
- Stress management techniques
- Problem-solving strategies
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Medication (e.g., antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications)
Treatment Options
Treatment for panic attacks and anxiety attacks typically involves a combination of therapy and medication:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to panic or anxiety attacks.
- Exposure therapy gradually exposes individuals to the situations or objects that trigger their attacks, helping them to develop coping mechanisms and reduce fear.
- Medication can be prescribed to help manage symptoms and prevent future attacks.
Distinguishing Between the Two
The following table summarizes the key differences between panic attacks and anxiety attacks:
| Panic Attacks | Anxiety Attacks | |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Sudden and intense | Gradual and persistent |
| Duration | Minutes to an hour | Hours to days |
| Symptoms | Physical (e.g., rapid heart rate, chest pain) and emotional (e.g., fear, panic) | Emotional (e.g., worry, nervousness) and physical (e.g., muscle tension, headaches) |
| Triggers | Stress, fear, specific situations or objects | Stress, everyday events or situations |
| Management | Deep breathing, relaxation techniques, CBT, exposure therapy, medication | Stress management, problem-solving strategies, CBT, medication |
Last Word
In the realm of mental health, panic attacks and anxiety attacks often intertwine, creating a complex tapestry of emotions. Understanding their differences is crucial for effective management and recovery. This comprehensive guide has shed light on the key distinctions, providing valuable insights and practical strategies to navigate these conditions with greater clarity and resilience.
FAQ Explained: Panic Attack Vs Anxiety Attack
What is the primary difference between a panic attack and an anxiety attack?
Panic attacks are characterized by a sudden onset of intense fear or discomfort, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, and dizziness. Anxiety attacks, on the other hand, are less severe and may be triggered by specific situations or stressors.
How can I distinguish between the two?
Consider the duration, intensity, and specific symptoms experienced during the attack. Panic attacks typically last for a shorter period (minutes) and are more intense, while anxiety attacks may persist for longer and exhibit milder symptoms.
What are some effective coping mechanisms for panic attacks?
Practice deep breathing exercises, engage in mindfulness techniques, and challenge negative thoughts. Seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can also provide valuable support and guidance.